 |
New York Architecture Images-Gramercy Park
Asser Levy Public Baths |
|
architect |
Arnold W. Brunner and William Martin Aiken |
|
location |
East 23rd Street at Asser Levy Place. |
|
date |
1908 Restored by the Parks Department in the late 1980s |
|
style |
Beaux-Arts recalled the style of ancient Roman baths and was inspired by the "City Beautiful" movement |
|
construction |
brick and limestone |
|
type |
Utility |
|
images |
  |
|
|
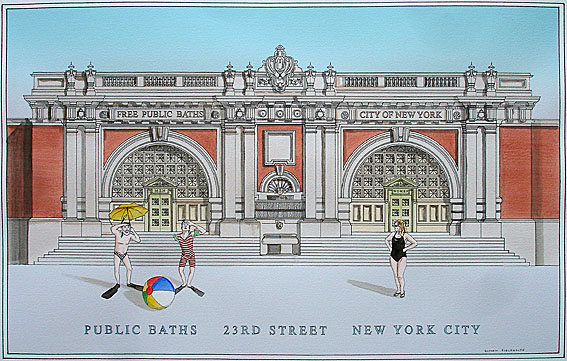 |
| Rendering copyright Simon Fieldhouse. Click here for a Simon Fieldhouse gallery. | |
|
Facilities at Asser Levy include indoor and outdoor pools, an Arts and Crafts room, an outdoor basketball court with adjustable hoops, and a playground designed to accomodate all ages. The indoor pool, one of New York's finest, boasts a gorgeous marble fountain shaped like a dolphin and a giant, and newly restored skylights. The outdoor pool, open from the beginning of July through labor day weekend, isn't nearly as nice, but it's a serviceable choice on a hot day. Classes are offered in swimming, martial arts, and guitar, among other choices. Call the center for a brochure, which changes frequently. Pool Hours are Monday through Friday from 7am-9pm, and Saturday and Sunday from 8am-4:45pm. Many of the older Recreation Centers (particularly those in Manhattan) were originally baths, including Asser Levy Recreation Center and Recreation Center 54. When Asser Levy opened in 1908, the facility was called the East 23rd Street Bathhouse. Designed by architects Arnold W. Brunner and William Martin Aiken, the building recalled the style of ancient Roman baths and was inspired by the "City Beautiful" movement, a turn-of-the-century effort to create civic architecture in the United States that would rival the monuments of the great European capitals. Recreation Center 54 opened on February 17, 1911, with 79 showers for men and 59 for women. The four-story, neo-classical building is currently undergoing a major capital reconstruction and I’ve been told by insiders that much of the building’s original details will be beautifully restored when it reopens. First Jewish Settlers (1654) New Amsterdam's Jewish CrusaderThe American tradition of religious freedom was not always a feature of early colonial life. Quakers, Lutherans, Catholics and Jews were vigorously expelled from the Puritan colonies in New England. Until 1759, Jews and Protestants were barred from French North America. Throughout the Spanish colonies, the Inquisition actively persecuted (and even executed) neo-Christians, converted Jews who proclaimed Catholicism but were suspected of secretly continuing the practice of their Judaism. Even the generally tolerant Dutch tried to exclude all but members of the Dutch Reformed Church from their American colonies. But the first Dutch Jews who settled in the capital, New Amsterdam, had much to do with altering the policy of intolerance. In 1654, 23 refugee men, women and children fleeing from the former Dutch colony of Recife, Brazil, landed in New Amsterdam. These Brazilian Jews were the descendants of perhaps 5,000 Jews who had been living in Recife, most of them secretly, since the mid-1500s. The Dutch captured portions of Brazil from the Portuguese in 1624, and some neo-Christians openly returned to the practice of their Jewish faith. When Portugal recaptured Brazil in 1654, these Jews feared the introduction of the Inquisition and fled. They were probably on their way back to Amsterdam after a stop in Jamaica when their ship was attacked by a Spanish privateer who stripped them of their valuables. A return to Europe was now out of the question. The refugees then made a deal with the ship's captain, Jacques de la Mothe, to take them to New Amsterdam, which they thought would be a hospitable destination. This was a one-sided bargain, struck in distress, and when the ship landed in New Amsterdam, De la Mothe filed suit against his passengers for failure to pay the balance of their passage. Peter Stuyvesant (1592-1672), the Dutch colonial governor with an anti-Semitic reputation, seized the Jews' meager possessions and ordered them sold at auction. When this failed to raise enough to meet their debts, he jailed two members of the group and wrote to the Dutch West India Company in Amsterdam, asking permission to expel the Jews. Stuyvesant noted that the Jews' indigence might make them a burden on the community and told the company that he “deemed it useful to require them in a friendly way to depart.” In a letter now in the archives of the AJHS, the Jews of New Amsterdam wrote to their fellow Jews in Holland asking for help. The latter petitioned the company on behalf of the New Amsterdam Jews, noting that Jews were allowed to reside in Holland and even to invest in the company. In April 1665, the company granted Jews permission to emigrate to and live in the colony, “so long as they do not become a burden to the company or the community.” Stuyvesant then tried another tack to discourage Jewish settlement. Stuyvesant importuned the colonial council to bar Jews from serving in the volunteer home guards. The council levied a special tax on Jews to pay for others to serve in their place. On November 5, 1655, Asser Levy and Joseph Barsimon filed petitions with the colonial court asking that they either be allowed to stand watch with the other citizens or relieved of the tax. After an initial rejection and a two-year fight, Levy won the right to stand watch. Levy, who had been one of the 23 refugees from Recife, would emerge as the champion of Jewish rights in New Amsterdam. When, in December 1655, Dutch troops captured the Swedish territory along the Delaware River, Stuyvesant refused to issue trade permits to Jewish settlers in the new territory. Levy and others wrote to their associates in Holland protesting this discrimination, and the company disciplined Stuyvesant for his actions. The company specified that, from then on, Jews in the colony were allowed to trade and own real estate, but not hold public office, open a retail shop, or establish a synagogue. In 1656, Levy was granted one of the first trading permits. In 1657, he was denied the right to practice a trade but petitioned this injustice and won. When he received his butchers license in 1661, it explicitly exempted him from having to slaughter pigs. When the English captured New Amsterdam in 1664 and renamed it New York, Levy swore an oath of allegiance to the British crown. All the rights he had under the Dutch were conferred to him under the new regime. In 1671, Levy was the first Jew to serve on a jury in North America. Asser Levy lies buried in an unknown grave. In tribute, a public school and a Brooklyn park bear his name. From his humble beginnings as a penniless refugee from Recife, Asser Levy became a prominent businessman, a crusader for religious equality and a defender of Jewish rights in New Amsterdam. Source: American Jewish Historical Society. |
|
|
links |
|